- Pulley Lagging
- QUICK LINKS
- Lagging Types Overview
- Product overview
- Lagging Select – Analysis Tool
- Lagging Analyst
- Pulley Lagging Specifications
- NAT v’s FRAS Overview
- Hot v’s Cold Bonding
- Large Lagging Rolls
- Pulley Lagging News
- Pulley Lagging Case Studies
- Storage Recommendations
- Material Safety Data Sheets
- Installations & Applicators
- Wear Panels
- About Us
- Case Studies
- LATEST CASE STUDIES & TECHNICAL PAPERS
- Technical Papers
- Technical Papers
- News
- LATEST NEWS
- MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
- MSDS Cold Bond Adhesive
- MSDS Cold Bond Adhesive Hardener
- MSDS Metal Primer 2205
- MSDS Metal Primer 2207
- MSDS Direct Bond Adhesive – Part A
- MSDS Direct Bond Adhesive – Part B
- MSDS Hot Vulcanised Brushing Cement
- MSDS Hot Vulcanised Lagging Adhesive
- MSDS High Temperature Direct Bond Adhesive Resin
- MSDS High Temperature Direct Bond Adhesive Hardener
- Elastotec Dangerous Goods Packing Details
- MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
- Partner Login
- APPLICATION
- Cold Bonded Lagging Application Procedure Steps
- Cold Bonded Ceramic Lagging Checklist
- Hot Vulcanised Application Procedure Steps
- Hot Vulcanised Ceramic Lagging Checklist
- Direct Bond Ceramic Pulley Lagging Application Procedure
- Direct Bond Ceramic Pulley Lagging Rolls <300mm
- Direct Bond Ceramic Lagging Checklist
- APPLICATION
- Contact



- Pulley Lagging
- QUICK LINKS
- Lagging Types Overview
- Product overview
- Lagging Select – Analysis Tool
- Lagging Analyst
- Pulley Lagging Specifications
- NAT v’s FRAS Overview
- Hot v’s Cold Bonding
- Large Lagging Rolls
- Pulley Lagging News
- Pulley Lagging Case Studies
- Storage Recommendations
- Material Safety Data Sheets
- Installations & Applicators
- Wear Panels
- About Us
- Case Studies
- LATEST CASE STUDIES & TECHNICAL PAPERS
- Technical Papers
- Technical Papers
- News
- LATEST NEWS
- MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
- MSDS Cold Bond Adhesive
- MSDS Cold Bond Adhesive Hardener
- MSDS Metal Primer 2205
- MSDS Metal Primer 2207
- MSDS Direct Bond Adhesive – Part A
- MSDS Direct Bond Adhesive – Part B
- MSDS Hot Vulcanised Brushing Cement
- MSDS Hot Vulcanised Lagging Adhesive
- MSDS High Temperature Direct Bond Adhesive Resin
- MSDS High Temperature Direct Bond Adhesive Hardener
- Elastotec Dangerous Goods Packing Details
- MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
- Partner Login
- APPLICATION
- Cold Bonded Lagging Application Procedure Steps
- Cold Bonded Ceramic Lagging Checklist
- Hot Vulcanised Application Procedure Steps
- Hot Vulcanised Ceramic Lagging Checklist
- Direct Bond Ceramic Pulley Lagging Application Procedure
- Direct Bond Ceramic Pulley Lagging Rolls <300mm
- Direct Bond Ceramic Lagging Checklist
- APPLICATION
- Contact

Pulley Lagging Analysis Tool
Introduction
Elastotec Australia, in collaboration with Conveyor Dynamics Inc. (CDI), has developed a new Lagging Analysis Tool, called Lagging select to quantify the complex interaction between the belt and the pulley lagging for both driven and non-driven applications.
Lagging select allows a detailed examination of:
- Traction utilization, including the determination of if and where localized slip will occur.
- Evaluation of the lagging and belt wear power, which causes wear when localized slip occurs.
- Defines the maximum level of shear stress applied to the belt and belt splices which can affect fatigue life.
- Evaluates the optimal selection of lagging type for a conveyor design to avoid inducing shear stress caused by incompatible belt and lagging stiffness.
- Evaluate the shear stress developed in the lagging at key locations to identify if the rubber and/or rubber adhesion bonds (ceramic tile and pulley steel) may fail prematurely.
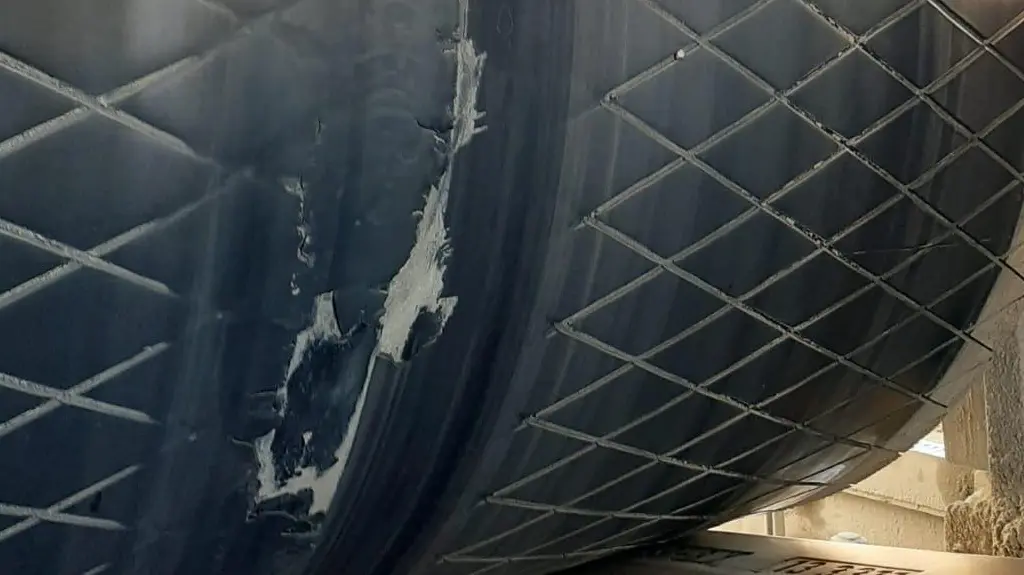
- Evaluate the effects of uneven lagging wear, belt cover wear and material buildup on both driven and non-driven pulleys, which results in differential shear and accelerated wear.
Usage and Benefits
- Selecting the optimal lagging type and design for a new or refurbished conveyor pulley evaluated for the specific conveyor design.
- Evaluating the cause(s) and/or contributing factors of premature lagging failure in an existing application.
- Evaluating an existing pulley lagging selection and quantifying the benefits of changing to an alternate lagging selection to improve belt and lagging wear life.
- Water and material shedding capabilities.
- Wear resistance.
Analysis Methods
- Lagging/belt contact interface
- Lagging tread root
- Pulley shell bond interface
- Ceramic tile bond interface

Add Your Tooltip Text Here
Add Your Tooltip Text Here
Add Your Tooltip Text Here
Add Your Tooltip Text Here
![]()
Contact Face: The surface of the lagging in contact with the belt cover
![]()
Tread Root: The base of the lagging profile, level with the grooves/sipes of the lagging
![]()
Pulley Shell: Where the lagging is adhered to the pulley shell
![]()
Tile Bond: The bond/adhesion of the ceramic tile into the rubber section of the lagging
Note: None of these factors should exceed 100% of their available utilization. It the limits are exceeded, it is predicted that lagging could fail in this area.
Analysis Results - Example
The laggingselect output is presented in a graphical format for review and interpretation by the designer, along with numerical results quantifying the utilization and magnitude of key selection factors:
Pulley Lagging Analyss: High Power, Drive Pulley, Dry Clean
Elastotec 38% Ceramic Dimpled, 12mm, 65 Duro

Lagging Envelope: Elastotec 38% Ceramic Dimpled, 12mm, 65 Duro

Analysis Results – Interpretation
The results of the Pulley Lagging Analysis are summarized on a plot representing the average normal pressure, shear stress and the developed friction between the lagging and the belt around the wrap angle between the belt entry and exit.
To assist in interpreting the analysis results, please refer to the following key points and example interpretation:
- The primary Y-Axis represents the Average Shear Stress and Normal pressure developed between the lagging and the belt.
- The secondary Y-Axis represents the effective friction factor developed as a function of Normal Pressure and Shear stress.
- The X-Axis represents the wrap position from the entry point T1 to the exit point T2 over the full wrap.
- The Available Driving Shear Stress (dry and wet) represent the upper limits as defined by the Variant Friction model and is a characteristic of the lagging material and geometry.

From the example plot above, the Shear Stress developed gradually increases around the pulley wrap with a corresponding decrease in Contact Pressure as the tension in the belt decreases towards the T2 exit. Localized belt slip will occur when the Shear Stress builds to a level where the Developed Friction intersects the Friction Limit lines. Both clean/dry and wet/dirty friction limits are represented.
An efficient lagging selection will show a progressive increase in Shear Stress around the full wrap with lower peak Shear Stress levels and friction requirements. A mismatch in the belt and lagging selection, primarily a mismatch in shear stiffness, can be caused by a lagging that is too stiff and resist the belts tendency to contract as the tension decreases around a drive pulley. This induces a shear stress which can exceed the friction available resulting in a greater localized slip.
Analysis Results – Interpretation of Lagging Performance Envelope
The Lagging Performance Envelope plot is a complex representation of the traction and shear stress fatigue limits of the lagging design evaluated. To assist in interpreting the envelopes developed please refer to the following key points and example interpretation:
- The Y-Axis represents the Average Shear Stress between the lagging and the belt.
- The X-Axis represents the Average Normal Contract Pressure between the lagging and the belt.
- The Available Driving Shear Stress (dry and wet) represent the upper limits as defined by the Variant Friction model and is a characteristic of the lagging material and geometry.
- The lines representing the fatigue stress limit at each of the key points represent the envelope., above which is indicative of excessive shear stress being developed in the lagging rubber at that key point.
- The Application line represents the nominal range of normal pressure and shear stress along the arc of contact between the belt entry point to the exit point, i.e. T1 and T2 conditions from the Pulley Lagging Analysis plot.
The percentage of utilization at each key point is also presented in the results.

From the example plot above, it can be interpreted that the application line is just within the performance envelope for the lagging example evaluated. However, the last approximate 20 degrees of contact arc before the belt exits the pulley @ T2 does indicate that the fatigue shear stress in the lagging rubber at both the tread root and tile bond locations is marginally exceeded.
This would indicate a fatigue life in these locations of slightly less than 5 years. It also indicates that under less than ideal (clean dry) conditions, the last 20 degrees of contact will have localized slip which can result in an increased rate of abrasion wear of both the lagging and belt.
Information Required
To perform a comprehensive conveyor analysis using laggingselect requires the following information for each pulley to be provided in either metric or us imperial units:
| PARAMETER | VALUE | UNITS |
|---|---|---|
| Conveyor Design | ||
| Belt Tension – T1 (incoming) | kN / kips | |
| Belt Tension – T2 (outgoing) | kN / kips | |
| Belt Speed | m/s / fpm | |
| Motor Power | kW / hp | |
| Belt Details | ||
| Belt carcass type (Steel or Fabric) | ||
| Belt Strength | kN/m / piw | |
| Belt Width | mm / in | |
| Pulley Details | ||
| Pulley Diameter (over shell) | mm / in | |
| Wrap Angle | Degrees | |
| Belt Cover in Contact Details | ||
| Cover Thickness | mm / in | |
| Cover Durometer (Shore A) | duro (A) | |
| Pulley Lagging Details | ||
| Lagging Type | ||
| Lagging Thickness | mm / in | |
| Lagging Durometer (Shore A) | duro (A) |
This information is typically contained within a conveyor design report and/or within conveyor and conveyor component equipment datasheets.
In cases where the existing belt or pulley contact covers are worn unevenly or exposed to material build-up then then additional information is required for a comprehensive analysis:
| PARAMETER | VALUE | UNITS |
|---|---|---|
| Material Buildup | Height mm / in | |
| Width mm / in | ||
| Belt Cover Wear | Height mm / in | |
| Width mm / in | ||
| Pulley Lagging Wear | Height mm / in | |
| Width mm / in |